Zoolied Inc.一 Optical Cylindrical Lenses
2025-7-25
A cylindrical lens is an optical lens that focuses light along a straight line rather than at a point. A plano-convex cylindrical lens consists of a flat surface and a convex cylindrical surface. It is commonly used to focus parallel or divergent light beams along a straight line or to alter the aspect ratio of an image.
Basic Characteristics of Cylindrical Lenses
A cylindrical lens is an optical element with a cylindrical surface. Unlike common spherical lenses, it has curvature in only one dimension, while the curvature is zero in the dimension perpendicular to it. This unique geometric characteristic enables cylindrical lenses to achieve asymmetric optical transformations, specifically designed for applications where it is necessary to alter the characteristics of a light beam in one direction while keeping the other direction unchanged. Based on surface shape, cylindrical lenses can be classified into various types, including plano-convex cylindrical lenses, plano-concave cylindrical lenses, biconvex cylindrical lenses, and meniscus cylindrical lenses.

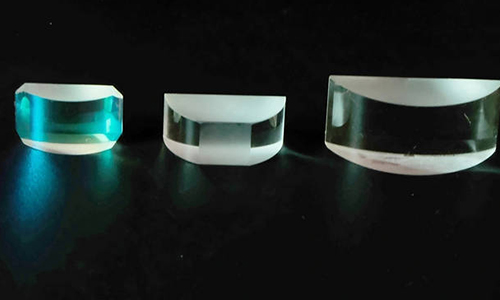
Basic Characteristics of Cylindrical Lenses
A cylindrical lens is an optical element with a cylindrical surface. Unlike common spherical lenses, it has curvature in only one dimension, while the curvature is zero in the dimension perpendicular to it. This unique geometric characteristic enables cylindrical lenses to achieve asymmetric optical transformations, specifically designed for applications where it is necessary to alter the characteristics of a light beam in one direction while keeping the other direction unchanged. Based on surface shape, cylindrical lenses can be classified into various types, including plano-convex cylindrical lenses, plano-concave cylindrical lenses, biconvex cylindrical lenses, and meniscus cylindrical lenses.


Optical Principles and Imaging Characteristics
The optical behavior of cylindrical lenses follows the law of refraction, but due to their asymmetric structure, their imaging characteristics differ significantly from those of spherical lenses. When parallel light beams are incident on a convex cylindrical lens, they converge into a focal line in the direction of curvature, while remaining parallel in the direction of no curvature. This characteristic makes cylindrical lenses particularly suitable for converting point light sources into line light sources or correcting astigmatism issues in optical systems. The focal length formula for cylindrical lenses is similar to that of spherical lenses, f = (n-1)/R, where n is the material refractive index and R is the cylindrical curvature radius. However, it is important to note that this formula applies only to the curvature direction of the cylinder.
Application Areas
Cylindrical lenses play an irreplaceable role in many fields. In laser technology, they are used for beam shaping in laser diodes, converting elliptical spots into circular spots; in barcode scanning systems, cylindrical lenses generate scan lines and collect reflected light; in display technology, they are used for generating line light sources in backlight modules; and in optical measurement, they are used for astigmatism correction and wavefront shaping. Additionally, cylindrical lens assemblies can be used to achieve optical systems with asymmetric magnification, finding widespread application in semiconductor inspection, material processing, and medical devices. With the advancement of precision optics, cylindrical lenses are also demonstrating significant value in emerging fields such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
#Cylindrical lens #Custom cylindrical lens #Cylindrical lens processing
The optical behavior of cylindrical lenses follows the law of refraction, but due to their asymmetric structure, their imaging characteristics differ significantly from those of spherical lenses. When parallel light beams are incident on a convex cylindrical lens, they converge into a focal line in the direction of curvature, while remaining parallel in the direction of no curvature. This characteristic makes cylindrical lenses particularly suitable for converting point light sources into line light sources or correcting astigmatism issues in optical systems. The focal length formula for cylindrical lenses is similar to that of spherical lenses, f = (n-1)/R, where n is the material refractive index and R is the cylindrical curvature radius. However, it is important to note that this formula applies only to the curvature direction of the cylinder.
Application Areas
Cylindrical lenses play an irreplaceable role in many fields. In laser technology, they are used for beam shaping in laser diodes, converting elliptical spots into circular spots; in barcode scanning systems, cylindrical lenses generate scan lines and collect reflected light; in display technology, they are used for generating line light sources in backlight modules; and in optical measurement, they are used for astigmatism correction and wavefront shaping. Additionally, cylindrical lens assemblies can be used to achieve optical systems with asymmetric magnification, finding widespread application in semiconductor inspection, material processing, and medical devices. With the advancement of precision optics, cylindrical lenses are also demonstrating significant value in emerging fields such as virtual reality and augmented reality.
#Cylindrical lens #Custom cylindrical lens #Cylindrical lens processing

